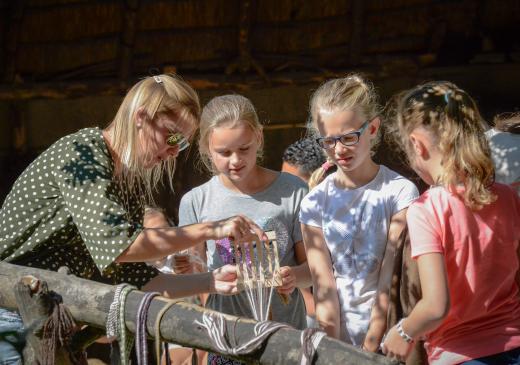-
Park
Roam through the prehistory, get very close to the Romans, discover Archeologyhouse of South Holland and dive into the Middle Ages. Step into the middle of history and discover how it used to be.
Read more -

-
Park
-
Overview
Roam through the prehistory, get very close to the Romans, discover Archeologyhouse of South Holland and dive into the Middle Ages. Step into the middle of history and discover how it used to be.
Read more -

-
Overview
-
Prehistory
-
Overview
8800 - 12 BC Travel along, far back in time to the camp of the hunter-gatherers, the first farmers, the Bronze Age and the Iron Age.
Activities
Read more
Sail in a real canoe, let yourself be painted like a real hunter, bake a prehistoric bun on stick, pull a heavy boulder stone and learn how to make a fire with a real flint. -

-
Overview
-
Middle Ages
-
Overview
406 - 1500 AD In the medieval town of Gravendam you live in the 14th century. Hard work is being done in the craft houses.
Activities
Read more
Make a candle at the imker, learn archery, show your sword fighting skills and make a bracelet from felt. -

-
Overview
-
Roman times
-
Overview
12 BC - 406 AD Visit the Roman village of Trajectum ad Rhenum and meet the Romans.
Activities
Read more
March in the Roman legion, enjoy a Roman arm massage in the bathhouse, make a nice fibula (Roman pin) and discover the Roman herbs. -

-
Overview
-
Practical information
-
Overview
Read all about our visiting hours, rates, route, contact details, parking, information for visitors with a disability, restaurants and the frequently asked questions.
Read more -

-
Overview
- Restaurants
-
Opening Times
-
Overview
View the opening days and times of Museumpark Archeon here.
Read more -

-
Overview
-
Zwammerdam Restoration Yard
-
Overview
After 40 years, the restoration of the Rijks Maritime Heritage Collection of Roman Zwammerdam ships began on Saturday 16 December 2017. In the restoration yard you follow the restoration of the six Roman Zwammerdam ships closely. In the restoration yard there is also a beautiful exhibition about the Zwammerdam ships, the Roman limes and the restoration.
The aim is to return these ships to the public in the newly established National Roman Shipping Museum, at Archeon, in the context of the Limes Unesco World Heritage Nomination.
Read more -
-
Overview
-
Vikings
-
Overview
We see three buildings, as contained in Dorestad around 800 AD.
Activities
Read more
Visit the Vikings and sail on their ship, learn how to make a rope and write your own name in runes. -

-
Overview
-
Archeologyhouse
-
Overview
The Roman museum in Archeon is housed in a reconstruction of a Gallo-Roman farmhouse. A variety of collections is on display. On the upper lever is Archeologyhouse South Holland, which exhibits the kinds of object discovered in the ground, from all periods, distant prehistory to early modern. The significance of all the items is explained by a special presentation. For example, an entire grave from the bronze age has been contructed, accompanied by the telling of a sensational story. This ares holds a number of worktables, where young visitors can learn more about archaeology by engaging in the work.
On the same level is the studio of Archeologische Werkgemeenschap Nederland (AWN), Rijnstreek chapter. This part is certainly also worth a visit. At weekend here, AWN volunteers study and interpret all kinds of material that has been found.
On the ground floor, you enter Archeon's Roman Museum, where the Roman period in the Netherlands is brought to life interactively. Display cases contain original acient Roman artefacts. Using films, touch screens and hands-on replicas, a living picture is drawn of the Romans and the original inhabitants at the time.
Read more -

-
Overview